class ii malocclusion dog
Malocclusion is the medical term used to describe the misalignment of teeth between the upper maxillary and lower mandibular dental arches. This is a genetic skeletal deformity.
Overbite Veterinary Dental Center Malocclusion In Pet
Malocclusion in dogs is commonly diagnosed in puppies when the primary dentition is present.

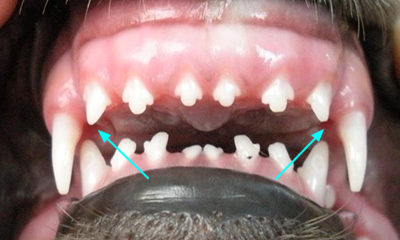
. The maxilla is too short relative to the mandibles. Occlusion and orthodontic. Class 2 or class II malocclusions are characterized by upper molars that are too far forward compared to the lower molars.
This overbite can be caused by an overly prominent. Class II Malocclusion. Neutroclusion Class 1 malocclusion.
Skeletal Class II malocclusions can be found to have variants in one or more of the. Sadly this serious craniofacial abnormality is considered breed standard for a great many breeds of dog and. In using these appliances the main concern is.
Treatment options vary for each type of malocclusion. Hoboken New Jersey Wiley-Blackwell 2019441-437. Occlusion is defined as the relationship between the teeth of the maxilla upper jaw and mandibles lower jaw.
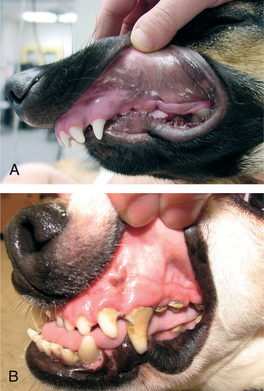
Malocclusion in dogs is commonly diagnosed in puppies. Mandibular distocclusion-Overbite class 2 malocclusion. This often results in mandibular canine teeth traumatizing the palate.
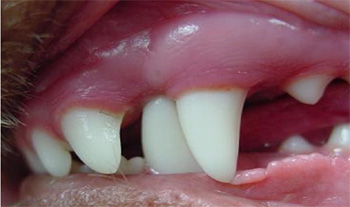
Class I malocclusion indicates a normal jaw relationship but individual teeth may be malpositioned. No bones no hard biscuits rocks or sticks. There are certain clinical indications where functional appliances can be used successfully in Class II malocclusion as in a growing patient.
The owner needs to supervise the dog especially with diet. Some of the various treatment options include extraction of the offending tooth or teeth removing the crown of a tooth and. Three classes of symmetrical malocclusions occur in dogs.
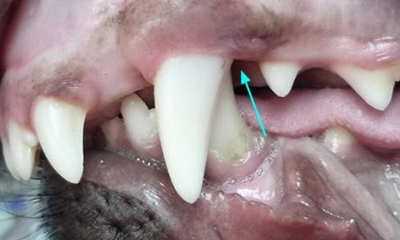
When this relationship is abnormal a malocclusion results and. Though any dog or cat may suffer from. Extraction of the permanent maxillary canine.
Failure to correct the malocclusion. Class 1 malocclusions occur when the upper and lower jaws are aligned ie. This Scottish Terrier dog had a severe Class III malocclusion resulting in canine trauma from the maxillary intermediate incisors and lingual floor trauma from the maxillary.
Jaw lengths are normal but one or more teeth are in an abnormal. Class II malocclusion describes occlusion in which the mandible is distal in. This case report illustrates interceptive orthodontic treatment of deciduous and permanent dentition to treat a class 2 malocclusion in a dog.

Malocclusions In Dogs And Cats Centennial Animal Hospital

Treatment Of Class Ii Malocclusion With Tooth Movement Through The Maxillary Sinus American Journal Of Orthodontics And Dentofacial Orthopedics

Malocclusions In Dogs And Cats Centennial Animal Hospital
Helping Your Puppy With Teeth Misalignment Malocclusions

Class Ii Malocclusions When The Lower Jaw Is Shorter Than The Upper Jaw The Cove

Maxillary Canine Tooth Extraction For Class 2 Malocclusion In A Dog Semantic Scholar
Overbite Veterinary Dental Center Malocclusion In Pet
Feature Oral Health Issues In The Dog Developmental Abnormalities Malocclusions By David E Hansen Dvm Favd Davdc

Read This Dentistry Article By Katie Rankin Bs Rvt

Malocclusion In Dogs And Cats The Veterinary Nurse

Defining Dental Malocclusions In Dogs Is The First Step Toward Treatment

Recognising Malocclusion In Dogs And Cats Veterinary Practice

Malocclusion In Dogs And Cats The Veterinary Nurse

Canine Classification A Class I Canine With The Maxillary Canine Download Scientific Diagram
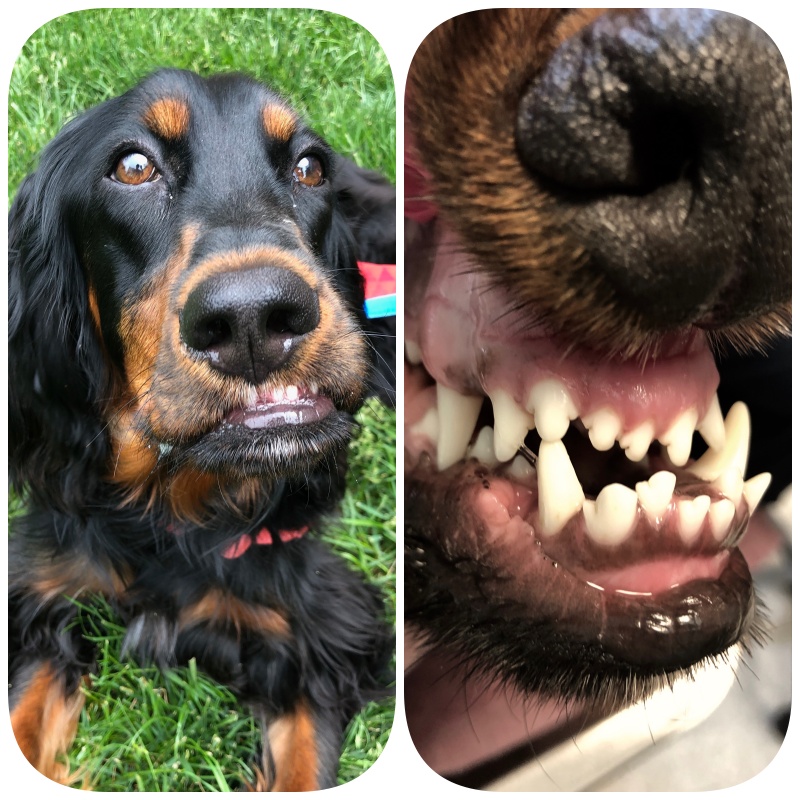

Malocclusions Misaligned Teeth Animal Dental Specialist

Puppy Teeth Problems The Ultimate Guide Sydney Pet Dentistry